Introduction to Sustainable Supply Chain
A 2024 Gartner survey found that 67% of supply chain leaders identify new ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) regulations as among their top five influential drivers for the next three to five years, highlighting the critical role of sustainability in future-proofing operations.
Sustainable supply chains have become a fundamental part of modern business, a holistic approach to managing the flow of goods and services from raw material sourcing to end-user delivery. This goes beyond traditional supply chain management by integrating environmental, social and economic considerations throughout the entire value chain.
A sustainable supply chain aims to reduce negative environmental impact, promote fair labour practices and ensure long-term economic viability. Its importance in today’s business cannot be overstated as consumers, investors and regulators are demanding more transparency and accountability from companies. Implementing sustainable supply chain practices helps businesses meet these expectations and also brings many benefits, including cost reduction through resource efficiency, brand reputation, risk management and innovation.
Sustainable supply chains also contribute to global efforts to address climate change, conserve natural resources and promote social equity. As businesses navigate a more complex and interconnected world, adopting sustainable supply chain practices is not just a moral imperative but a strategic necessity for long-term success and resilience in the face of global challenges.
Key Components of a Sustainable Supply Chain
Sustainability Certifications
Sustainability certifications play a key role in supply chain sustainability by providing a standardized framework for assessing and verifying environmental, social and economic practices throughout the entire production process. These certifications, such as Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance and Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), are powerful tools for companies to demonstrate their commitment to responsible sourcing and ethical business practices. By adhering to strict criteria and undergoing regular audits, certified organizations can improve transparency, build consumer trust and differentiate themselves in the market.
Moreover, certifications drive positive change within industries by encouraging suppliers to adopt more sustainable practices, reduce their environmental footprint and improve working conditions for labourers. This ripple effect can lead to widespread improvements across entire supply chains, long-term sustainability and resilience. But it’s important to note that while certifications are valuable, they should be seen as part of a broader sustainability strategy rather than a standalone solution. Companies must continually evaluate and improve their practices beyond certification requirements to achieve lasting supply chain sustainability.
Traceability and Transparency
Traceability and transparency have become fundamental elements in modern supply chain management, especially in an era where consumers are more conscious about the origin and journey of their products. Implementing robust tracking systems for materials and processes throughout the supply chain not only ensures quality control and efficiency but also builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
GoBolt, for example, integrates real-time tracking and customer-facing delivery visibility across its fulfillment and last-mile ecosystem, ensuring both merchants and shoppers can see exactly where their order is.
By being transparent in the supply chain, companies can quickly identify and address issues, reduce risks and demonstrate their commitment to ethical and sustainable practices. This level of visibility allows businesses to make informed decisions, optimize operations and respond to market demands or regulatory changes.
Moreover, a transparent supply chain can be a powerful marketing tool, differentiating a brand in a competitive market and appealing to consumers who value honesty and accountability. As technology advances, tools like blockchain and IoT devices are making it easier than ever for businesses to achieve end-to-end traceability, so this practice is more important than ever in today’s economy.
Supplier Audits and Relationships
In today’s global market, businesses are recognizing the importance of sustainability across their supply chains. Conducting regular supplier audits is a key step in ensuring your partners adhere to sustainability standards and your company’s values. These audits not only identify potential risks and areas for improvement but also demonstrate your commitment to responsible sourcing.
But audits alone are not enough. Building strong relationships with suppliers is equally important as it encourages open communication, collaboration and mutual growth. By working with suppliers, companies can provide support, share best practices and co-create solutions to sustainability challenges. This collaborative approach not only enhances compliance but also drives continuous improvement and long-term sustainability performance across the entire supply chain. So the combination of rigorous audits and nurturing supplier relationships is the foundation for sustainable practices and a more resilient and responsible business ecosystem.
Ethical and Responsible Sourcing
Ethical and responsible sourcing has become a key aspect of modern business practices, especially in industries that rely heavily on raw materials and global supply chains. As consumers become more aware of the social and environmental impacts of their purchases, companies are under more pressure to ensure their materials are sourced in ways that respect human rights and fair labour practices. This goes beyond compliance with regulations; it means actively investigating and monitoring supply chains, partnering with ethical suppliers and implementing transparent reporting mechanisms.
By prioritizing ethical sourcing, businesses not only benefit workers and communities in source countries but also mitigate risks of reputation damage and legal issues. Moreover, responsible sourcing leads to more sustainable and efficient supply chains, benefiting the company and the environment in the long run. So integrating ethical considerations into procurement strategies is no longer just a moral imperative but a key factor in building a resilient and socially responsible business model.
Environmental Aspects
Carbon Emissions and Footprint
As sustainability becomes a global focus, businesses are recognizing the importance of reducing carbon emissions and minimizing their carbon footprint. Effective strategies to achieve this are critical for both environmental and long-term business success. Some key approaches include optimizing transportation routes to reduce fuel consumption, investing in energy-efficient warehouses and distribution centres and partnering with suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. Companies can also look into alternative fuel sources such as electric or hydrogen-powered vehicles for their logistics operations. Moreover, embracing digital technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things can help streamline processes, reduce waste and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
By taking a holistic approach to carbon reduction, businesses can not only reduce their environmental impact but also enhance their reputation, reduce costs and stay ahead of changing regulations. As consumers become more eco-conscious, companies that prioritize sustainable supply chain practices will be better placed to meet market demands and gain a competitive advantage in the long run.
GoBolt is a leader in low-emissions delivery, completing over 40% of last-mile shipments using electric vehicles. With data-backed emissions tracking and route optimization technologies, GoBolt helps its merchants reduce their Scope 3 transportation emissions without compromising performance.
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy
Energy efficiency and renewable energy are two key components in the fight against climate change and the pursuit of sustainable development. Energy efficiency means optimizing energy consumption in buildings, industries and transportation systems through insulation, smart technologies and energy-saving appliances. This reduces carbon emissions and saves businesses and households significant costs. At the same time, the adoption of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydroelectric and geothermal power is rapidly changing the global energy landscape.
These clean energy alternatives offer a sustainable solution to meet growing energy demands while minimizing environmental impact. Governments, businesses and individuals are increasingly recognizing the importance of transitioning to renewable energy, driving innovation and investment in the sector. By combining energy efficiency with renewable energy, we can create a more sustainable and resilient energy future, reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate the effects of climate change for generations to come.
Waste Reduction and Management
Waste reduction and management are key components of a sustainable supply chain. Companies can implement various methods to reduce waste generation and manage it responsibly. One approach is to adopt lean manufacturing principles to optimize production processes and reduce excess materials. A robust inventory management system can prevent overproduction and spoilage. Circular economy principles such as designing products for easy disassembly and recycling can reduce waste significantly. Partnering with suppliers to reduce packaging and use of recyclable materials is another effective way.
Companies should also invest in waste segregation systems and partner with recycling facilities to ensure proper disposal of different waste streams. Additionally, data-driven waste tracking and analysis can help identify areas for improvement and measure the impact of waste reduction initiatives. By implementing these across the supply chain, businesses can not only reduce their environmental impact but also improve operational efficiency and reduce costs associated with waste management.
Biodiversity and Environmental Impact
Supply chain activities have far-reaching consequences on biodiversity and the environment, often beyond the immediate operational areas. From resource extraction to manufacturing, transportation and waste disposal, each stage of the supply chain can contribute to habitat destruction, pollution and climate change. For example, deforestation for agricultural expansion or raw material sourcing directly threatens countless species and disrupts entire ecosystems. Industrial processes and logistics operations emit greenhouse gases and other pollutants affecting air and water quality globally.
As consumers become more aware of these issues, businesses are under increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices and reduce their ecological footprint. This means implementing responsible sourcing policies, optimizing transportation routes to reduce emissions and investing in clean technologies. By considering the environmental impact of their supply chain activities, companies can play a critical role in preserving biodiversity, mitigating climate change and ensuring a more sustainable future for our planet.
Economic and Social Dimensions

Economic Viability
In today’s fast-changing business environment, being economically viable while being sustainable is a major challenge for organizations across industries. The key is to find a balance between environmental responsibility and financial success. Companies must recognize that sustainability initiatives are not just ethical obligations but also drivers of long-term profitability and competitiveness. By integrating sustainability into their core business strategies, organizations can reduce operational costs, enhance brand reputation and tap into growing markets for green products and services. This not only ensures compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations but also positions businesses to capitalize on emerging opportunities in the green economy.
Moreover, investors and consumers are increasingly favouring companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, making it a key factor in staying relevant and growing in the future. Ultimately, the most successful businesses will be those that see sustainability not as a constraint but as a driver of innovation, efficiency and long-term success.
Social Responsibility and Human Rights
In today’s global economy, businesses have a critical responsibility to ensure their supply chains uphold social responsibility and human rights standards. This goes beyond mere compliance with local laws; it means actively promoting ethical practices, fair labour conditions and respect for human dignity at every stage of production and distribution. Companies must do due diligence, partner only with suppliers who share these values and demonstrate a genuine commitment to worker welfare. This means fair wages, safe working conditions, reasonable working hours and freedom from discrimination and exploitation.
Moreover, businesses should invest in programmes that empower local communities, support education and skill development and contribute to sustainable development goals. By prioritizing social responsibility and human rights across their supply chains, companies not only mitigate risks and enhance their reputation but also contribute to building a more equitable and sustainable global economy. This creates a positive ripple effect, improving lives, driving innovation and long-term business success and setting a higher standard for corporate citizenship in the 21st century.
Fair Labour Practices
Fair Labour Practices across the supply chain is a critical part of responsible business in today’s global market. Companies must prioritize the well-being and rights of workers at every stage of production, from raw material sourcing to manufacturing and distribution. This means implementing robust policies and procedures to prevent exploitation, ensure safe working conditions and fair wages and benefits. Audits, supplier assessments and third party certifications play a key role in verifying compliance with labour standards.
Moreover, open communication channels with workers and local communities help to identify and address issues promptly. By upholding fair labour practices across the entire supply chain, businesses not only meet their ethical obligations but also enhance their reputation, mitigate risks and contribute to sustainable economic development in the regions where they operate.
Innovative Approaches and Strategies

Innovation in Sustainable Supply Chain
In today’s fast-changing business environment, companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of integrating sustainability into their supply chain. By leveraging new innovations, organisations can not only reduce their environmental impact but also improve efficiency and long term profitability. From blockchain for enhanced traceability to AI for route optimization, the opportunities for sustainable supply chain innovation are vast and exciting. Companies are using IoT sensors to monitor and reduce energy consumption in warehouses, advanced analytics to minimize waste and overproduction, and circular economy principles to extend product lifecycles.
Moreover, the rise of 3D printing and localised manufacturing is disrupting traditional supply chain models, reducing transportation emissions and enabling more customer centric production. As consumers become more environmentally aware, businesses that adopt these sustainable practices will not only contribute to a greener future but also gain a competitive edge. The challenge now is to integrate these technologies and approaches into existing supply chain frameworks, which requires continuous learning, adaptation and collaboration across industries.
Circular Supply Chain and Economy
The concept of circular supply chain and economy is a game changer in how businesses manage resources and waste. By adopting circular economy principles, companies can create a closed loop supply chain that maximises resource efficiency and minimises environmental impact. This means designing products for longevity, reusability and recyclability, and implementing systems for product recovery, refurbishment and remanufacturing. In a circular supply chain, materials and resources are continuously cycled back into the production process, reducing the need for virgin materials and waste.
This not only helps companies reduce costs and their environmental footprint but also creates new business opportunities in areas such as reverse logistics, product-as-a-service models and innovative recycling technologies. As consumers become more eco-aware and regulations around sustainability tighten, embracing circular economy principles in supply chain management is becoming not just a competitive advantage but a necessity for long term business success.
Sustainable Packaging and Materials
In today’s eco-conscious world, sustainable packaging and materials are a key focus for businesses looking to reduce their environmental impact. Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of adopting eco-friendly alternatives to traditional packaging methods. This means using biodegradable, recyclable or compostable materials such as plant-based plastics, recycled paper and innovative solutions like mushroom packaging. Many brands are also embracing minimalist designs that use less material overall, while others are developing reusable or refillable packaging systems.
By prioritizing sustainable packaging, businesses not only reduce waste and conserve resources but also appeal to environmentally aware consumers. Moreover, sustainable packaging can lead to cost savings in the long run through reduced material use and improved logistics. As technology advances and consumer demand grows, we can expect to see even more innovative and Earth-friendly packaging solutions emerge, paving the way for a greener future in product packaging and material use.
Governance and Compliance
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance is a key part of modern business, especially when it comes to environmental and social regulations. As governments and international bodies introduce stricter guidelines to address climate change, social inequality and other pressing issues, companies must stay on top of these requirements. Compliance not only helps businesses avoid fines and legal trouble but also shows their commitment to responsible practices and ethical behaviour.
To ensure compliance, organisations should have robust internal systems for monitoring and reporting, conduct regular audits and invest in employee training programmes. Moreover, staying up to date with changing regulations and industry best practice is essential for maintaining compliance in an ever changing landscape. By prioritizing compliance, companies can protect their reputation, mitigate risks and contribute to a more sustainable and equitable future for all stakeholders.
Corporate Governance and Risk Management
Corporate governance and risk management are key components of a successful and sustainable business strategy. In today’s complex and fast-changing business world, organizations must have robust governance structures to identify, assess and mitigate potential risks while ensuring long-term sustainability. This means having clear lines of accountability, a culture of transparency and comprehensive risk management frameworks that align with the company’s overall objectives. By embedding these into their operational DNA, businesses can improve decision making, protect stakeholder interests and maintain compliance.
Moreover, effective corporate governance and risk management can lead to operational efficiency, investor confidence and reputation in the market. As organisations face more diverse challenges from cyber threats to environmental issues, the ability to adapt and respond to emerging risks becomes critical. By prioritizing corporate governance and risk management, companies can not only protect their assets and stakeholders but also position themselves for sustainable growth and success.
Performance Measurement and Improvement
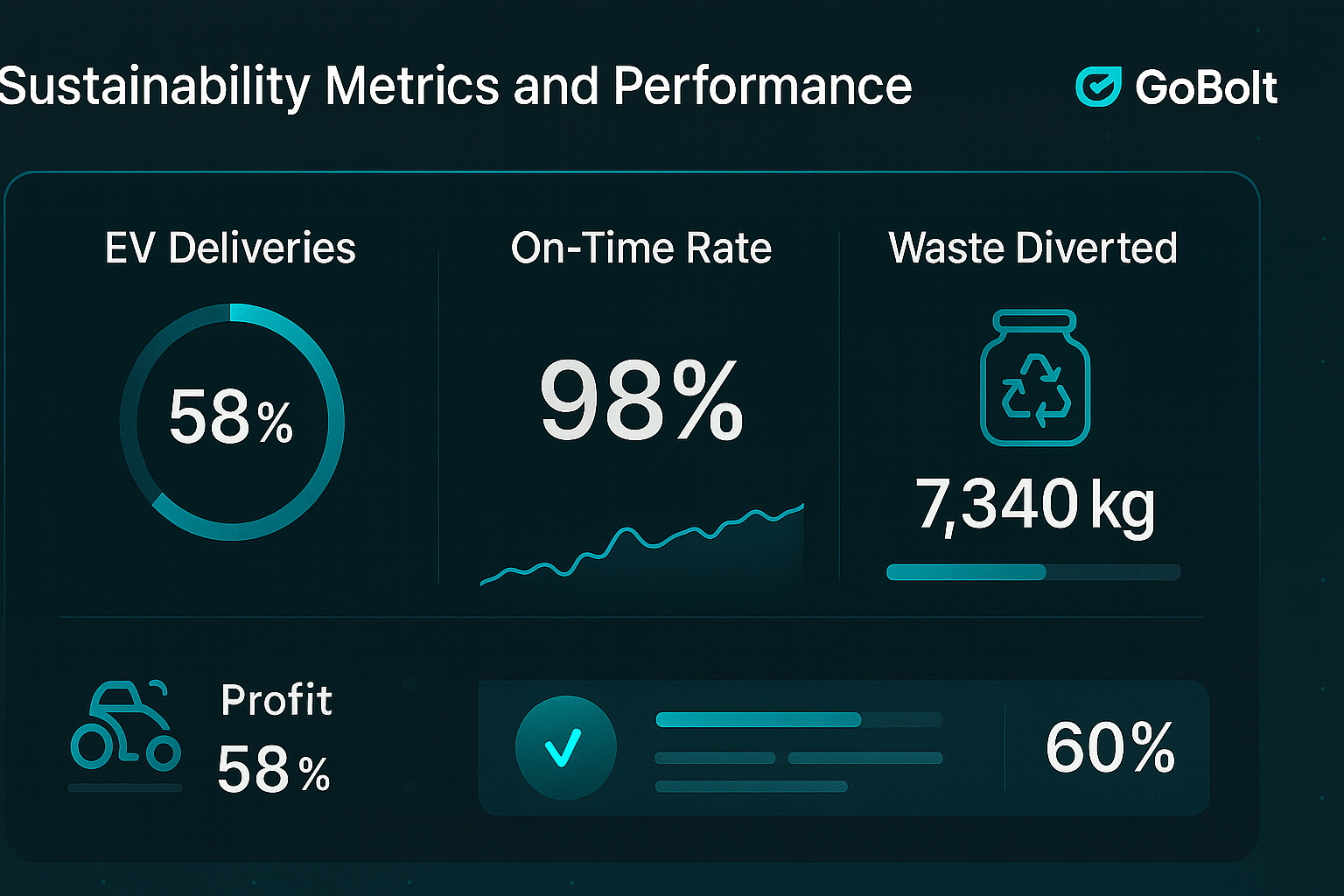
Sustainability Metrics and Performance
Sustainability is no longer a buzzword but a key part of business success. To manage and improve sustainability, companies need to have robust metrics and performance indicators. These key metrics are a compass, guiding organisations towards their sustainability goals and providing tangible evidence of progress. By tracking carbon emissions, water usage, waste reduction and social impact, businesses can gain insight into their environmental and social footprint.
Moreover, these metrics enable companies to identify areas for improvement, set realistic targets and benchmark against industry standards. Regular monitoring and reporting of sustainability metrics drives internal improvement and enhances transparency and credibility with stakeholders including customers, investors and regulatory bodies. As sustainability becomes more and more part of business strategy, using data driven metrics is essential for organisations to measure, manage and continuously improve their sustainability performance in a meaningful and impactful way.
Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder engagement is key for organizations to align their sustainability goals and practices with the expectations and needs of various interested parties. By engaging with employees, customers, investors, suppliers and local communities, companies can gain insight, build trust and create a shared vision for sustainable development. This collaborative approach not only enhances transparency and accountability but also innovation and risk/opportunity identification. Engaging stakeholders throughout the sustainability journey enables organizations to develop more robust strategies, implement more effective initiatives and achieve greater impact.
Moreover, it allows co-creation of solutions to complex environmental and social challenges while meeting business objectives. By prioritising open dialogue, active listening and responsive action, companies can build strong relationships with their stakeholders, leading to better decision making, increased support for sustainability and ultimately a more resilient business model.
Conclusion
As this article highlights, sustainability in the supply chain is no longer optional. GoBolt embodies this shift by building a logistics model designed to scale without compromise. In 2025, sustainability is a strategic advantage, with businesses prioritizing ESG due diligence to meet investor and consumer demands. Data from LRQA’s EiQ platform indicates that companies with robust sustainability programs achieve a 10% higher market valuation.
In today’s global economy implementing a sustainable supply chain is more than just a trendy buzzword – it’s a business necessity. As consumers become more environmentally aware and regulations tighten, companies that put sustainability in their supply chain are future proofing themselves. A sustainable supply chain reduces environmental impact, drives innovation, improves operational efficiency and enhances brand reputation. By focusing on responsible sourcing, optimising transportation networks and minimising waste, businesses can reduce their carbon footprint and costs.
Moreover, a sustainable approach builds stronger relationships with suppliers, customers and stakeholders and creates a ripple effect of positive change throughout the entire value chain. In an era where transparency and corporate responsibility are key, companies that adopt sustainable supply chain practices demonstrate their commitment to ethical business and global citizenship. This attracts and retains environmentally conscious consumers and investors who are increasingly considering sustainability metrics in their decision making. Implementing a sustainable supply chain is good for the planet – it’s a strategic advantage that drives growth, resilience and long term profitability in a competitive global market.