Reverse Logistics: What It Is & Why It Matters
Reverse logistics is a part of supply chain management that deals with moving products from customers back to businesses. This includes returns, repairs, refurbishment, recycling and proper disposal. Unlike traditional logistics, which moves products forward to customers, reverse logistics ensures goods are handled efficiently on the way back. When done right, it helps businesses recover value, boost sustainability initiatives and customer satisfaction. With e-commerce on the rise and environmental responsibility becoming more important than ever, optimizing reverse logistics is more crucial than ever.
GoBolt, a leading provider of sustainable supply chain solutions, integrates reverse logistics into its operations, offering customers a more responsible, tech-driven way to manage returns and asset recovery.
What Is Reverse Logistics?
Reverse logistics is managing the journey of products, materials and information from the point of consumption back to the point of origin. It includes returns, repairs, refurbishments, recycling and responsible disposal. As sustainability and cost efficiency become more important, reverse logistics gives businesses a way to minimize waste, cut costs and improve operational agility.
At GoBolt, reverse logistics services are aligned with its commitment to carbon neutrality. The company’s platform uses data and AI-driven insights to optimize returns management, minimize environmental impact and operational efficiency.
Why It Matters in Modern Supply Chains
Straits Research reports that the global reverse logistics market is projected to reach $947.36 billion by 2032, growing at a 5.18% CAGR, driven by increasing e-commerce returns and sustainability demands. A good supply chain is key to competitiveness. Reverse logistics plays a big role in reducing landfill waste, strengthening customer loyalty and achieving ESG goals.
GoBolt’s 100% carbon-neutral deliveries from mid-2023 show how reverse logistics can serve both profit and sustainability in a rapidly changing market.
Key Components of Reverse Logistics
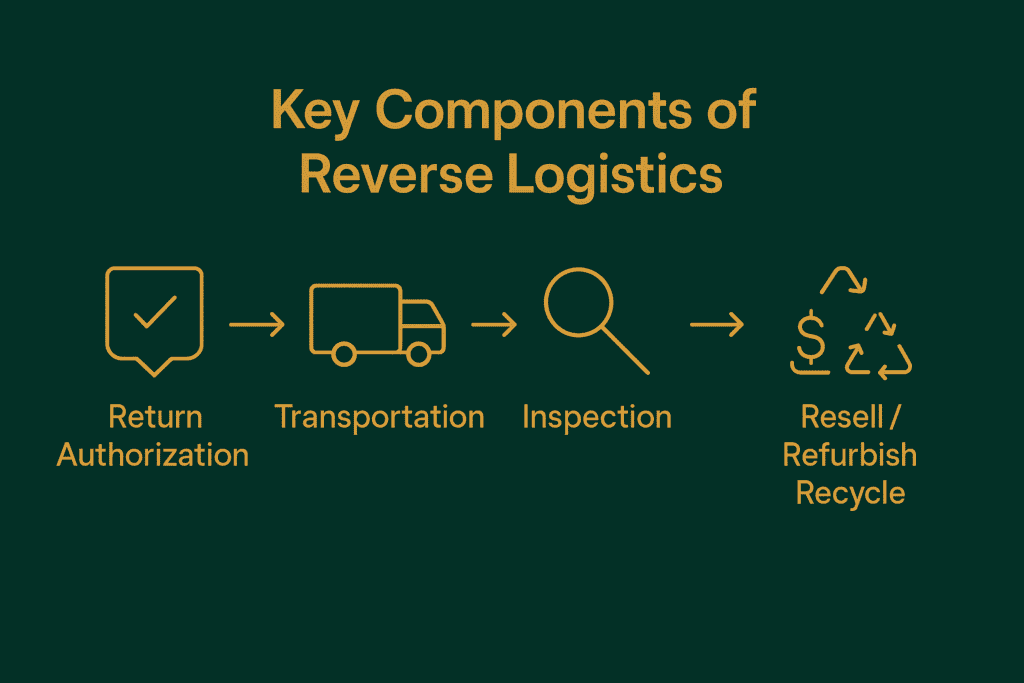
How Reverse Logistics Works
The reverse logistics process involves: return authorization, transportation, inspection, sorting and final disposition (resell, refurbish, recycle or dispose). Efficiency at each step minimizes costs, maximizes value recovery and customer experience.
Using GoBolt’s integrated fulfillment and transportation network, businesses can achieve a closed-loop logistics where returned goods are seamlessly reintegrated into inventory or sustainably disposed of.
Managing Product Returns
A smooth and customer-friendly returns process builds trust and repeat business. By using real-time tracking and flexible return solutions, GoBolt enhances the customer experience and provides businesses with valuable insights into product performance and customer preferences.
Recovering Asset Value
Asset value recovery is key. Companies can resell, refurbish or recycle returned products to minimize losses and maximize profit. According to BDO Insights (2024), effective reverse logistics can recover up to 20% of a product’s original value. GoBolt’s technology-driven approach enables smart decision-making so goods are directed to the most profitable and sustainable channels.
Reverse Logistics Processes
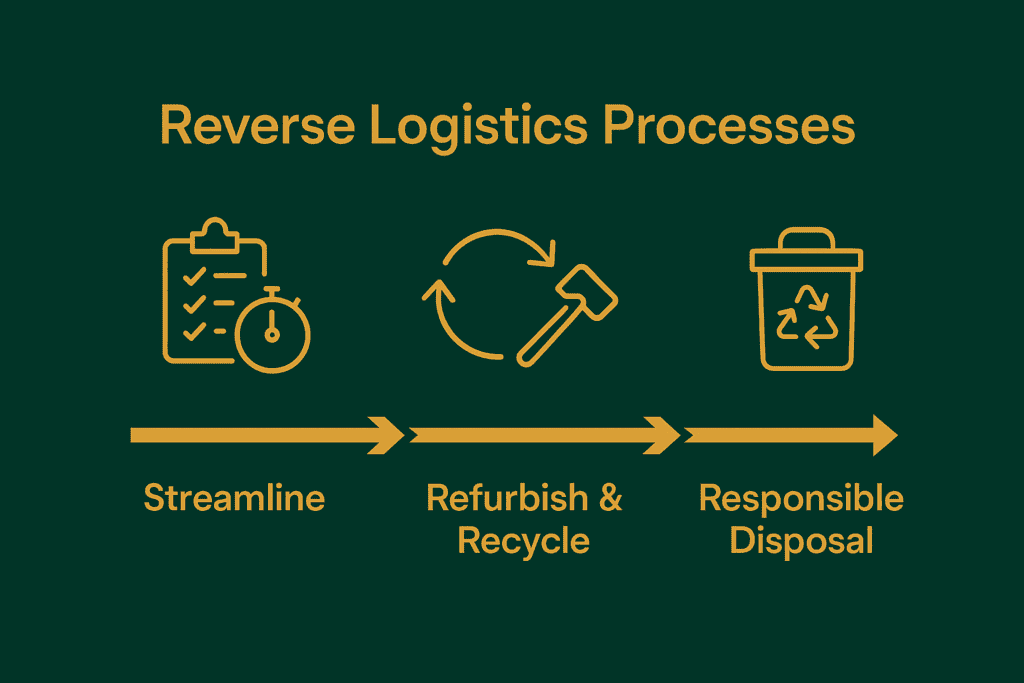
Streamlining the Returns Process
Automation and real-time data make returns processing more efficient and transparent. GoBolt’s platform offers smart return routing and consolidated logistics, reducing costs and turnaround times.
Refurbishment & Recycling
Refurbishing extends a product’s life while recycling mitigates environmental impact. GoBolt’s sustainability-first mission aligns with these practices, so returned goods are processed with a minimal carbon footprint, whether refurbished for resale or responsibly recycled.
Responsible Disposal
When products can’t be reused, proper disposal is essential. GoBolt partners with eco-conscious recyclers and waste processors to ensure sustainability standards are met and landfill is minimized.
Building an Effective Reverse Logistics Strategy
Creating a Strong Reverse Logistics Plan
A solid plan starts with analyzing return data, setting clear policies and leveraging technology. Businesses that optimize their reverse logistics processes can reduce costs and improve sustainability.
Best Practices for Reverse Logistics
- Simplify the returns process
- Use data to track and analyze returns
- Partner with third-party logistics providers for efficiency
- Implement sustainable recycling and disposal methods
- Integrate reverse logistics with the overall supply chain strategy
Challenges in Reverse Logistics
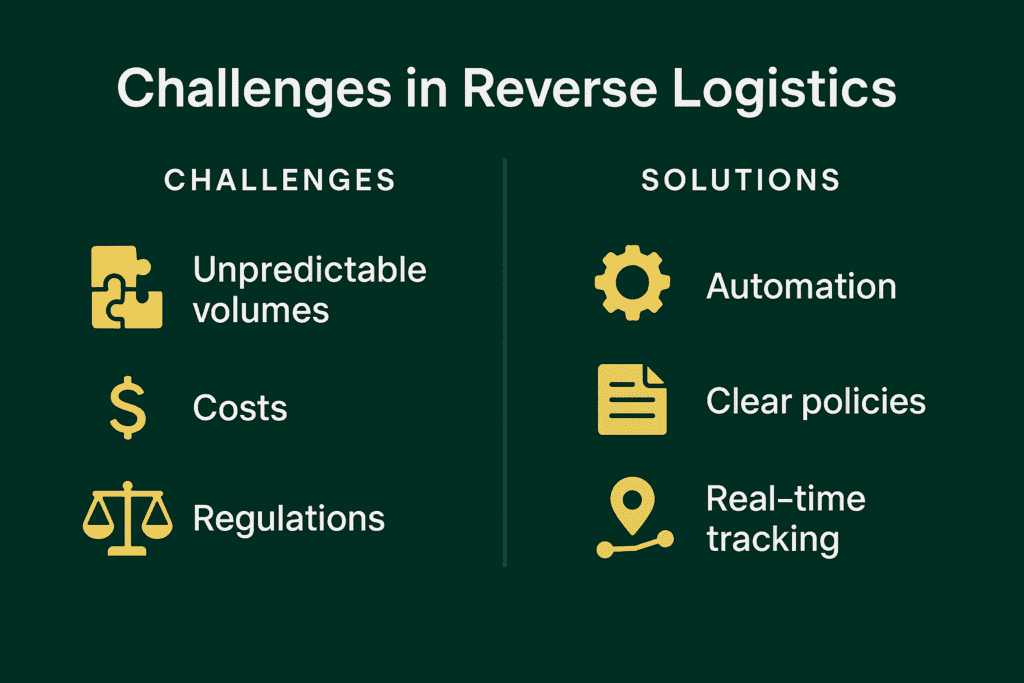
Overcoming Common Obstacles
Managing returns efficiently is challenging due to unpredictable return volumes, high costs and quality control concerns. Businesses need clear policies and advanced tracking systems to keep operations smooth.
Navigating Regulations
Increasing global regulations on waste disposal and product recalls make compliance critical.
GoBolt ensures clients meet regulatory standards through transparent, certified recycling and disposal practices.
For example, in 2025, EU regulations on waste disposal will get stricter, and 3PLs will have to enhance reverse logistics compliance to avoid fines averaging $50,000 per violation, according to IOSCM.
Balancing Costs & Profitability
Reverse logistics can be costly, but a well-optimized process reduces unnecessary costs while maintaining service quality. Businesses need to find the right balance between cost reduction and operational efficiency.
The Role of Technology in Reverse Logistics
How Tech Improves Reverse Logistics
Technology plays a big role in improving efficiency. AI-powered forecasting, IoT tracking and cloud-based platforms help businesses streamline their reverse logistics operations.
Tracking & Data Analytics
Real-time tracking and data give businesses visibility into return patterns to make informed decisions to minimize losses.
Enhancing Customer Experience
A seamless returns process improves customer satisfaction and loyalty. Investing in automation and self-service returns makes it easier for customers and reduces operational costs.
Reverse Logistics Across Industries
How Different Sectors Handle Returns
Retail, manufacturing and logistics providers all use reverse logistics to improve efficiency and reduce waste. Leading brands use automation and AI to manage returns better.
Real-World Case Studies
Businesses that have strong reverse logistics recover value, reduce costs and improve customer experience. Looking at industry leaders provides best practices and innovation.
Reverse Logistics & Sustainability
Supporting the Circular Economy
Reverse logistics is key to the circular economy by extending product life through repair, refurbishment and recycling. This reduces waste and conserves resources.
Environmental Benefits
Reducing landfill waste, lowering carbon footprint and recycling materials all contribute to a more sustainable business model. Sustainable companies get a competitive advantage and meet customer expectations.
Final Thoughts
Reverse logistics is no longer an afterthought – it’s a must-have. Businesses that optimize their reverse logistics will see cost savings, sustainability and better customer relationships. By 2030, the 3PL market, heavily reliant on reverse logistics, will be $1.78 trillion, with sustainability driving 40% of the growth according to Mordor Intelligence.
Companies that adopt technology, refine their return policy and prioritize sustainability will be better equipped to handle the demands of modern supply chains. The future of reverse logistics is about efficiency, sustainability and customer experience.







